How Organic Farming Promotes Health, Ecology, and Global Leadership
Organic farming keeps nature clean and abundant with life. When you visit an organic farm, you’ll notice a vibrant environment buzzing with animals, birds, and insects. Research highlights that ecological farms host about 30% more wildlife and plants compared to conventional farms. This is largely due to the absence of harmful pesticides and the minimal use of fertilizers.
The COVID-19 pandemic has shifted focus towards organic food, emphasizing its role in ensuring safety and nutrition. People are now prioritizing healthy food that strengthens the immune system, highlighting the importance of nutritional security rather than just food security, which often focuses on carbohydrates alone.
Among various healthy options, organic food has become a preferred choice, especially since the pandemic. Organically grown foods are known to contain higher levels of antioxidants, essential micronutrients, and no harmful chemicals, pesticides, or synthetic fertilizers. They also offer better taste and, most importantly, contribute to the planet’s sustainability by maintaining ecological balance.
This shift to organic food not only promotes personal health but also supports the environment, making it a win-win for individuals and the planet.
India stands out among 187 countries practicing organic agriculture, according to the FiBL survey 2021. The country is home to 30% of the world’s total organic producers and has an impressive 2.30 million hectares of organically cultivated land. With 27,59,660 farmers (including 11,60,650 under PGS and 15,99,010 under India Organic), 1,703 processors, and 745 traders, India holds a significant place in global organic farming.
In recent years, the country has witnessed a remarkable increase in organic agricultural land, reflecting the growing adoption of sustainable farming practices. This rapid expansion highlights India’s commitment to eco-friendly agriculture and its potential to lead the world in organic farming innovations.
Indian Organic Agriculture Statistics for last 10 years (2011-12 to 2020-21)
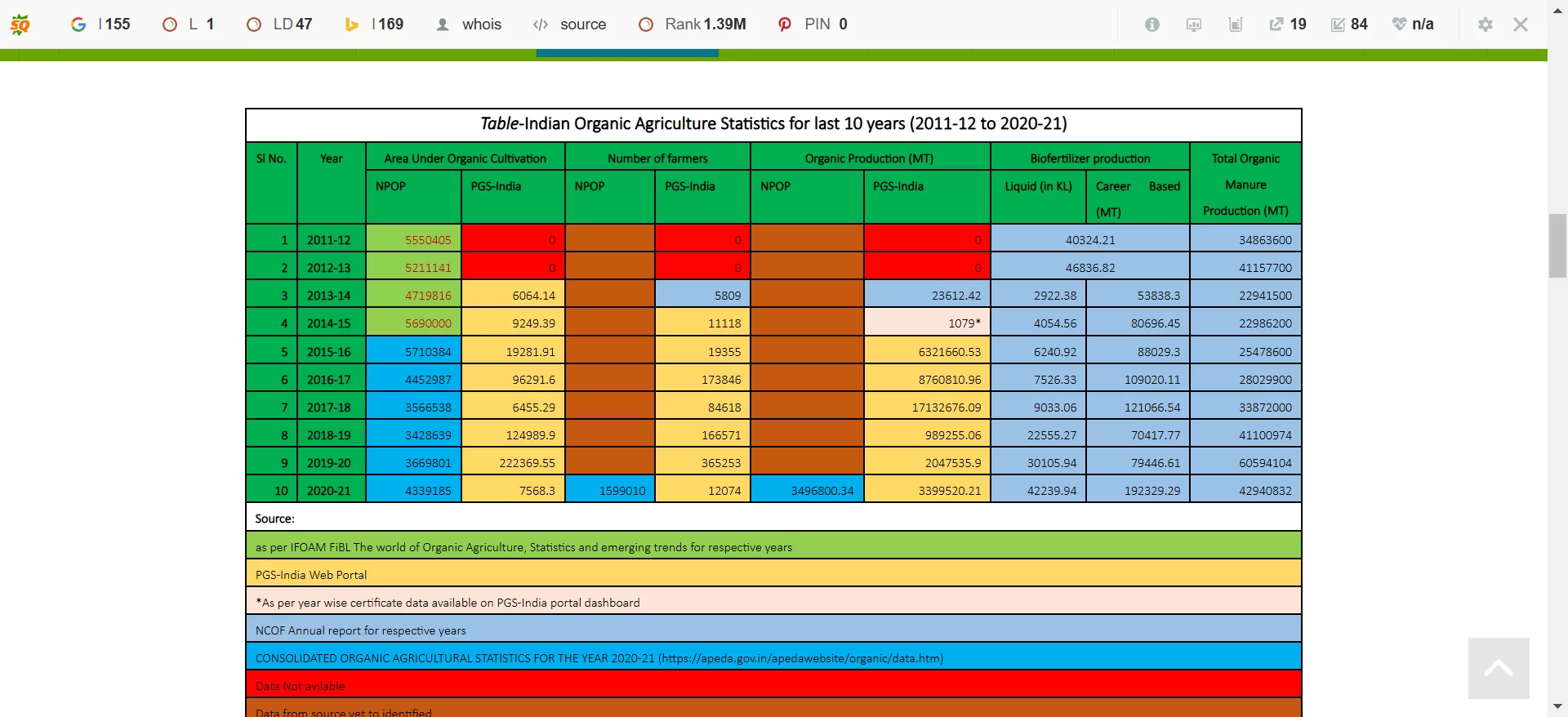
Image Reference https://nconf.dac.gov.in/StatusOrganicFarming
What Organic Farming Means?
Organic farming emphasizes eco-friendly practices like composting, crop rotation, and the use of natural fertilizers to grow crops without synthetic chemicals. This approach supports soil fertility, biodiversity, and environmental health by minimizing pollution and reducing reliance on chemical inputs.
In India, sustainable methods align closely with traditional agricultural practices. Coconut husk products like cocopeat, coconut husk, and coco coir have gained importance due to their ability to retain moisture, improve soil aeration, and eliminate the need for synthetic fertilizers.
Sustainable agriculture focuses on maintaining healthy ecosystems by utilizing natural processes and eco-friendly inputs. This practice promotes biodiversity, enhances soil fertility, and minimizes environmental degradation.
Classroom Impact
In schools, organic farming is taught as an agricultural method that avoids chemicals. Students learn the importance of natural fertilizers like compost and the role of crop rotation in maintaining soil fertility and preventing pollution. This early education lays the foundation for future eco-conscious farming practices.



A Brief History of Organic Farming in India
Sustainable agriculture has deep roots in India, where farmers historically relied on natural fertilizers like animal manure and crop residues. However, the modern movement toward sustainable agriculture gained momentum in the early 2000s, driven by increasing consumer awareness and government support.
Contribution of Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh emerged as a leader in sustainable agriculture, becoming India’s largest producer of eco-friendly products like organic pulses and grains. Its farmers adopted environmentally conscious practices for crops like soybean, wheat, and lentils, serving as a model for other states.
Today, Madhya Pradesh not only leads in organic crop production but also relies on eco-friendly products like cocopeat. Trusted coco peat suppliers in India provide high-quality growing mediums that are integral to these sustainable practices.
Sikkim- India’s First Fully Organic State
Sikkim holds the distinction of being the first fully organic state in India, achieving this milestone in 2016. The state government initiated the journey toward organic farming in 2003 by implementing the Sikkim Organic Mission. Through a systematic ban on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, Sikkim transitioned all its agricultural land to organic practices.
Key Achievements in Sikkim
- 100% Organic Certification: Every acre of farmland in Sikkim is certified organic under standards such as NPOP (National Program for Organic Production).
- Economic Benefits: Organic farming boosted the state’s agri-tourism sector, attracting visitors interested in eco-friendly farming practices.
- Environmental Impact: The ban on chemicals resulted in healthier soil, cleaner water, and increased biodiversity.
- Flagship Crops: Sikkim’s organic produce includes ginger, cardamom, oranges, and other horticultural crops, which are in high demand domestically and internationally.
Tamil Nadu- A Hub for Cocopeat and Sustainable Practices
Tamil Nadu has emerged as a major contributor to organic farming, particularly through the production and use of cocopeat, coconut husk, and coir-based products. These natural by-products play a crucial role in improving soil health and water retention, making them integral to sustainable farming practices.
Key Contributions of Tamil Nadu
- Cocopeat Production: Tamil Nadu is a global leader in producing and exporting cocopeat, a sustainable growing medium made from coconut husks. It is widely used in organic farming for its moisture-retention properties.
- Training and Awareness: Various agricultural universities and NGOs in Tamil Nadu actively promote organic farming through farmer training programs on composting, crop rotation, and biofertilizer use.
- Adoption of Biofertilizers: Tamil Nadu farmers extensively use biofertilizers and compost to reduce dependency on synthetic inputs, enhancing both crop yields and environmental health.
- Flagship Crops: Organic produce from Tamil Nadu includes bananas, turmeric, groundnuts, and vegetables, which have seen increasing demand in urban and export markets.
Tamil Nadu’s focus on organic farming aligns traditional agricultural practices with modern sustainability techniques, making it a key player in India’s organic agriculture landscape.
Why Organic Farming Crucial Today
- Ensuring Food Safety and Environmental Health:
Chemical-free crops reduce the risk of pesticide contamination, making food safer for consumption while protecting the environment. - Growing Demand for Organic Products:
The demand for eco-friendly agricultural products is surging both domestically and internationally. Indian crops like organic tea, spices, and vegetables are gaining popularity among health-conscious consumers. - Reducing Chemical Use:
Sustainable agriculture minimizes the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, preventing soil and water contamination and safeguarding ecosystems.
Growth of Organic Production in India
| Sl No. | Year | Organic Production (MT) |
| 1 | 2014-15 | 1,079* |
| 2 | 2015-16 | 6,321,660.53 |
| 3 | 2016-17 | 8,760,810.96 |
How Organic Farming Works
1. Key Practices
- Crop Rotation: Prevents pest infestations and improves soil fertility.
- Green Manure: Plants like legumes are used to replenish nitrogen in the soil.
- Biofertilizers and Compost: Organic materials are used to enrich the soil naturally.
2. Role of Coco Coir and Cocopeat
- Cocopeat retains moisture, reducing the need for frequent watering.
- Coconut husks enhance soil aeration, encouraging healthy root growth.
- Coco coir serves as a versatile growing medium for container gardening, reducing reliance on soil.
Real-World Impact- Success Stories
Farmers in Tamil Nadu, for example, have significantly increased their crop yields by integrating cocopeat into their farming practices. A case study of a small-scale strawberry farmer highlights how switching to cocopeat, not only boosted production but also reduced water usage by 30%.
Can Eco-Friendly Farming Feed the World?
Potential to Support Food Security
Organic Farming has the potential to support global food needs, though it may require more land and labor than conventional practices.
Challenges in Scaling
Despite its benefits, scaling sustainable agriculture faces hurdles, such as higher production costs and limited market access for farmers.
Profitability and Use Cases in India
Profitable Crops in India
- Vegetables: Organic tomatoes and spinach fetch high prices in urban markets.
- Spices and Herbs: Turmeric and basil are in demand locally and internationally.
- Fruits: Organic mangoes cater to a niche but profitable market.
2. Regions Adopting Sustainable Agriculture
- Sikkim: India’s first fully organic state.
- Madhya Pradesh: A leader in sustainable soybean and wheat production.
- Rajasthan and Maharashtra: Focus on organic cotton and fruit cultivation.
Can Green Agriculture Replace Conventional Farming?
While Eco-friendly farming provides environmental benefits, it faces challenges in matching the productivity of conventional methods.
Sustaining Indian Farming with Hybrid Practices
Combining eco-friendly products like coco coir with modern technologies can ensure high productivity and environmental sustainability. Government incentives can further encourage farmers to shift toward sustainable methods.
Eco-friendly agriculture, also known as green farming, offers solutions to many of the challenges posed by conventional agriculture. It ensures healthier food, promotes biodiversity, and reduces environmental damage. Products like cocopeat, coconut husks, and coco coir play a key role in these practices by improving soil health and conserving water.
The future of sustainable agriculture in India depends on innovation, collaboration, and consumer awareness. As more people embrace these practices, the agricultural sector will move toward a greener, healthier, and more sustainable future.
As sustainable agriculture continues to grow, the role of eco-friendly products like cocopeat, provided by trusted coco peat manufacturers,exporters or suppliers in India, will remain pivotal in promoting soil health and conserving water.

